A. Introduction — Why Every Pharma Student Must Know Research Areas
Often, pharmacy students study subjects like Pharmaceutics, Pharmacology, Pharmaceutical Chemistry, and Analysis,
but a common confusion arises:
“Sir, where are all these subjects used practically?”
The syllabus is completed, exams are passed, but students don’t have a clear picture of:
• which subject is linked to which type of research or job,
• which area would suit their interests,
• and what they should choose in the future—industry, academia, clinical field, or regulatory side.
When you know about different research areas, it helps you:
• ✅ Choose a specialization (for M. Pharm / PhD)
• ✅ Select a project topic (at the UG/PG level)
• ✅ Gain career clarity — whether you want to go into industry, teaching, clinical research, or regulatory affairs.
Most importantly, the research journey can start right from the UG level —
with a curiosity, a “why,” a doubt.
The student who wants to understand not just the syllabus, but the logic behind the concepts,
has already taken the first step into the world of research.

👉 So remember:
“You don’t need to be a researcher to know about research, but you must know about research to become a successful pharmacist.”
In this blog, we will talk about the Top 10 Research Areas that every pharmacy student should know about — so that you can make your future decisions with clarity, not confusion.
B. Top 10 research areas for Pharma Students
Research Area 1: Drug Discovery & Development
Whenever we take a tablet, capsule, or injection, we rarely think:
“How was this drug made?”
Drug Discovery & Development is the field that works to answer this very question.
It is considered the foundational area of pharmacy research — this is where a drug’s journey begins.
🔍 What is Drug Discovery & Development?
In simple terms, this process involves:
• Understanding the root cause of a disease
• Identifying a target for that disease (enzyme, receptor, gene, etc.)
• Designing new chemical entities
• Checking their efficacy, safety, and toxicity
• And finally, bringing a potential drug to the market

💡 Why is this Area Important?
• New diseases are emerging, and drug resistance is increasing
• There is a need to improve existing drugs
• Pharma companies need innovative molecules
Who Should Choose This Area?
This area is best for students who:
• Have an interest in both chemistry and biology
• Have a long-term research mindset
🎯 Career Opportunities
With a drug discovery background, you can go into:
• R&D departments of pharma MNCs
• Drug discovery startups
• CROs (Contract Research Organizations)
• PhD → Scientist / Research Lead roles
• International research labs
📚 Related Subjects & Skills
For this area, you should have strong skills in:
• Medicinal Chemistry and Biochemistry
• Molecular biology (basic level)
• Computer skills (for molecular modelling – bonus)
Drug discovery sounds glamorous, but it demands patience and consistency.
Success doesn’t come overnight, but when it does — the impact is global. “Every successful drug you see today was once just a risky idea in a research lab.”
Research Area 2: Pharmaceutical Biotechnology
Today’s pharmaceutical industry is not limited to just small chemical drugs.
Vaccines, insulin, monoclonal antibodies, gene-based therapies — all of these fall under Pharmaceutical Biotechnology.
🔍 What is Pharmaceutical Biotechnology?
Pharmaceutical Biotechnology means:
• Using living systems (cells, bacteria, yeast) to manufacture drugs
• Biological products such as:
o Vaccines
o Recombinant proteins (Insulin, Growth hormone)
o Biosimilars

💡 Why is This Area Important?
• The world is rapidly moving towards biologics
• Biotech drugs are essential for cancer, autoimmune diseases, and rare genetic disorders
• The market for vaccines and biologics is growing every year
👉 In the future, a large part of the pharma industry will be the biopharma industry.
Who Should Choose This Area?
This area is perfect for students who:
• Are interested in biology, genetics, and cell culture
• Are excited by innovation and future technologies
After Pharmaceutical Biotechnology, you can go into:
• Biopharma & vaccine companies
• Research labs (India & abroad)
• PhD → Scientist roles
• Biotech startups
Related Subjects & Skills
For this field, you should have strong skills in:
• Biotechnology
• Microbiology
• Biochemistry
• Molecular biology (basic to intermediate)
• Aseptic techniques & documentation
Research Area 3: Formulation & Drug Delivery Systems (NDDS)
Pharmacy is not limited to just discovering drugs —
how, when, and in what quantity the drug is delivered into the body is equally important.
What is Formulation & Drug Delivery Research?
The main focus of this research area is:
• Converting the drug into the best possible dosage form
• Improving the bioavailability of the drug
• Delivering the drug in a controlled, targeted, and safe manner
• Increasing patient acceptability
Novel Drug Delivery Systems (NDDS)
Developing better and smarter delivery systems than traditional dosage forms.
Examples:
• Controlled release tablets (once-a-day dosing)
• Targeted drug delivery (delivering the drug only to the affected organ)
• Nano-drug delivery systems (nanoparticles, liposomes)
• Transdermal patches
• Inhalation systems (asthma, COPD)
The aim of NDDS is:
✔ To increase the effect of the drug
✔ To reduce side effects
✔ To improve patient compliance
🎯 Controlled Drug Delivery
Controlled drug delivery means:
• The drug is released slowly and continuously
• Blood concentration remains constant
🎯 Targeted Drug Delivery
Targeted delivery means: Delivering the drug directly to the disease site, instead of spreading it throughout the entire body.
Examples:
• Cancer therapy (tumor-specific delivery)
• Brain-targeted drug delivery
• Colon-targeted systems
🔬 Nano-Drug Delivery Systems
Nano-drug delivery is the most advanced and exciting area of pharmaceutical research.
In this, the drug is converted into nano-sized particles:
💡 Why This Research Area is Extremely Important
There is a simple logic behind all this research: Same drug + Better delivery = Better therapy
Research Area 4: Pharmaceutical Analysis & Analytical Method Development
- The pharmaceutical industry has a golden rule:
- “A drug is only as good as its quality.”
- And who proves the quality of a drug?
👉 Pharmaceutical Analysis.
Pharmaceutical Analysis means:
• Confirming the identity of the drug
• Checking its purity, strength, and quality
• Detecting impurities and degradation products
The core work in this field is analytical method development and validation.

🧪 Analytical Method Development – Simple Meaning
Analytical method development means:
Creating a reliable, accurate, and reproducible method that allows the drug to be analyzed repeatedly with the same results, so that we can learn about the API in the dosage form, the presence of impurities, and the drug’s stability.
📐 Method Validation (As per ICH)
Simply developing a method is not enough. It also needs to be validated according to ICH guidelines.
Key validation parameters:
• Accuracy
• Precision (intra-day, inter-day)
• Linearity
• Robustness
• Ruggedness
• LOD & LOQ
💡 Why This Research Area Is Extremely Important
Without pharma analysis:
• ❌ Drugs cannot be approved
• ❌ Regulatory clearance is not obtained
• ❌ Patient safety cannot be guaranteed
No analysis = No approval = No business
🏭 Role in Pharma Industry
Pharmaceutical Analysis is directly linked to:
• Quality Control (QC)
• Quality Assurance (QA)
• Stability studies
• Regulatory submissions
• Bioequivalence & dissolution studies
Who Should Choose This Area? This research area is best suited for students who:
• Enjoy working with instruments
• Possess accuracy, discipline, and a mindset for following Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
• Like documentation and data analysis
🎯 Career Opportunities
After studying Pharmaceutical Analysis, you can pursue careers as:
• Quality Control Analyst
• Analytical R&D Scientist
• Method Development Specialist
• Stability Study Analyst
• Work in CROs & testing laboratories

📚 Subjects & Skills Required
To excel in this field, you need:
• Strong basics in Pharmaceutical Analysis
• Knowledge of instrumental techniques
• Knowledge of ICH guidelines
• Data interpretation skills and software handling
• Documentation and report writing
Research Area 5: Pharmacology & Translational Research
Pharmacy doesn’t just teach you how to make drugs, it also teaches you what drugs do inside the body.
👉 Understanding the drug’s effect, side effects, safety, and dose-response — this is all the work of Pharmacology.
🔬 What is Pharmacology & Translational Research?
Pharmacology research focuses on:
• Drug’s mechanism of action
• Drug–receptor interaction
• Dose–response relationship
• Therapeutic effect vs. toxicity
It involves the study of:
• In-vitro models (cell lines, isolated tissues)
• In-vivo models (animal models)
• Disease-specific experimental models
Translational research means:
The journey of a drug from the lab bench to the patient’s bedside.
🔄 Why Is It Called Translational Research?
Many discoveries remain limited to the lab.
Translational research ensures that:
• Lab findings are clinically relevant
• The drug’s effect can be predicted in humans
• Clinical trials are scientifically justified
💡 Why This Research Area Is Extremely Important
Pharmacology is incomplete without a translational approach because:
• The next step after drug discovery is pharmacology
• Clinical trial design depends on pharmacological data
• Safety margins are decided here
High-demand areas:
• Cancer pharmacology
• CNS disorders (depression, epilepsy, Alzheimer’s)
• Cardiovascular & metabolic diseases
🎯 Career Opportunities
After Pharmacology & translational research:
• Pharmacology R&D scientist
• Preclinical research associate
• Clinical research support roles
• PhD → Academia / Research institutes
• Teaching profession
The international scope in this field is also quite strong. 📚Subjects & Skills Required
To be strong:
• Pharmacology (basic + advanced) and Pathophysiology
• Biostatistics (basic)
• Experimental design understanding and scientific writing
Research Area 6: Clinical Research & Pharmacovigilance
When a drug successfully passes laboratory and animal studies,
the most important question arises:
“Is this drug safe and effective for humans?”
Clinical Research answers this question, and once the drug is on the market, Pharmacovigilance ensures its continuous safety.

🔬 What is Clinical Research?
• Scientific evaluation of the drug on humans
• Conducting clinical trials (Phase I–IV)
• Assessing safety, efficacy, and dosage
Phases of clinical trials:
• Phase I: Safety & tolerability (healthy volunteers)
• Phase II: Efficacy & dose optimization
• Phase III: Large-scale confirmation
• Phase IV: Post-marketing studies
This process is conducted under ethical guidelines, protocols, and regulations.
What is Pharmacovigilance?
Pharmacovigilance focuses on:
• Detecting Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs)
• Monitoring drug safety after marketing
• Risk–benefit analysis
In simple terms:
“Keeping an eye on the drug’s safety even after it’s on the market.”
Example:
• Reporting new side effects
• Identifying drug–drug interactions
• Updating label warnings
💡 Why This Research Area Is Critically Important
• Human life is directly involved
• Regulatory bodies give the highest priority to safety data
• One serious ADR can change a drug’s future
Who Should Choose This Area?
This field is best for students who:
• Have a patient-centric mindset
• Documentation & data analysis is your favourite
• Communication skills are strong
🎯 Career Opportunities
After clinical research & pharmacovigilance:
• Clinical Research Associate (CRA)
• Clinical Trial Coordinator
• Drug Safety Associate
• Pharmacovigilance Officer
• Medical Reviewer (with experience)
, 📚Subjects & Skills Required
To be strong in this field:
• Clinical pharmacy basics and Pharmacology
• Biostatistics (basic) and Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines
Important skills:
• Communication and Documentation
• Attention to detail
Research Area 7: Regulatory Affairs & Regulatory Science
Developing a drug is a scientific challenge, but bringing that drug to market legally is an even bigger challenge. If regulatory approval is not obtained, no matter how effective the drug is —
it simply cannot be launched in the market. That’s why it’s said in the pharma industry:
“No approval = No product = No business.”

What is Regulatory Affairs & Regulatory Science?
Regulatory Affairs means:
• Understanding the drug approval process
• Following the rules of regulatory authorities
• Presenting scientific data in a regulatory format
The work of regulatory professionals involves:
• Preparing dossiers (CTD / eCTD)
• Submitting ANDA, NDA, MA applications
• Responding to queries (deficiency letters)
• Handling audits and inspections
🌍 Regulatory Authorities You Should Know Important authorities for pharmacy students:
• USFDA (USA)
• EMA (Europe)
• CDSCO (India)
• MHRA (UK)
Every country has its own rules, and regulatory science applies those rules with scientific logic.
💡 Why This Research Area Is Extremely Important
• Global pharma companies launch products in multiple countries
• Export is not possible without regulatory compliance
• Even a small mistake can delay or reject drug approval
Who Should Choose This Area?
This area is best for students who:
• Prefer less lab work and more desk-based scientific work
• Like guidelines, rules, and SOPs
• Are interested in documentation and compliance
• Target corporate pharma roles
Career options after Regulatory Affairs:
• Regulatory Affairs Executive
• Regulatory Submissions Specialist
• Compliance Officer
• Regulatory Strategy Associate
📚 Subjects & Skills Required
To be strong in this field:
• Pharmaceutical Analysis (basic)
• Pharmaceutics & stability studies
• Knowledge of regulatory guidelines
• Scientific & technical writing
Important skills:
• Documentation accuracy
• Communication with authorities
• Audit readiness
Research Area 8: Pharmacogenomics & Personalized Medicine
Today, a very important question is being raised in pharmacy:
“Same drug, same dose — will it work for every patient?”
The answer is — No.
And this concept gives rise to Pharmacogenomics & Personalized Medicine.
This research area represents the future of pharmacy.
What is Pharmacogenomics?
Pharmacogenomics means:
• Studying the relationship between genes and drugs
• Understanding how genetic variation causes:
o A drug to work well in some patients
o To work less effectively in others
o And to cause severe side effects in some

In simple words:
“Every patient has a different genetic makeup, therefore the response to each drug is also different.”
💊 What is Personalized Medicine?
In this approach, treatment is tailored according to the patient’s:
• Genes
• Age
• Gender
• Lifestyle
• Disease condition
💡 Why This Research Area Is Extremely Important
Traditional medicine approach:
One drug fits all ❌
Modern approach:
One drug fits one patient ✅
The importance of this area:
• In cancer therapy, personalized treatment is lifesaving
• In psychiatric drugs, the response is highly variable
• In cardiovascular and anticoagulant therapy, dose personalization is critical
In the future:
• Trial-and-error prescribing will decrease
• Adverse drug reactions will be reduced
• Treatment outcomes will improve
Future of pharmacy = Precision medicine
Who Should Choose This Area?
This area is best for students who:
• Have an interest in genetics and molecular biology
• Are future-oriented and innovation-driven
• Are interested in both research and clinical application
• Want international research exposure
🎯 Career Opportunities
After Pharmacogenomics:
• Advanced research labs
• Genomics & biotech companies
• Clinical research (specialized roles)
• PhD & international postdoctoral research
Countries like the USA, Europe, and Japan are already heavily investing in this field.
📚Subjects & Skills Required
To be strong in this area:
• Genetics & molecular biology and Biochemistry
• Pharmacology (advanced) and Bioinformatics (basic level)
Important skills:
• Data interpretation
• Understanding genetic reports
Research Area 9: AI, Data Science & Bioinformatics in Pharma
Today’s pharma industry is no longer limited to test tubes and labs.
Now, pharma has a strong connection with computers, data, and algorithms.
Therefore, a new powerful research area has emerged:
What Does This Research Area Actually Mean?
In this research area, computers are used to:
• Speed up drug discovery
• Virtually screen millions of molecules
• Analyze biological data (genes, proteins)
• Extract patterns from clinical and real-world data
In simple words:
“What takes years in the lab, AI can do in a few months or weeks.”
Role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Pharma
AI is used in:
• Identifying new drug targets
• Predicting structure–activity relationships
• Predicting side effects and toxicity in advance
• Drug repurposing (old drugs, new uses)
📊 Role of Data Science in Pharma
Data science helps in:
• Identifying trends
• Analyzing drug effectiveness
• Detecting safety signals
• Better decision-making
Data-driven decisions = safer and smarter healthcare
🧬 What is Bioinformatics?
Bioinformatics means:
• Analyzing biological data through computers
• Studying DNA, RNA, and protein sequences
• Understanding gene–disease and gene–drug relationships
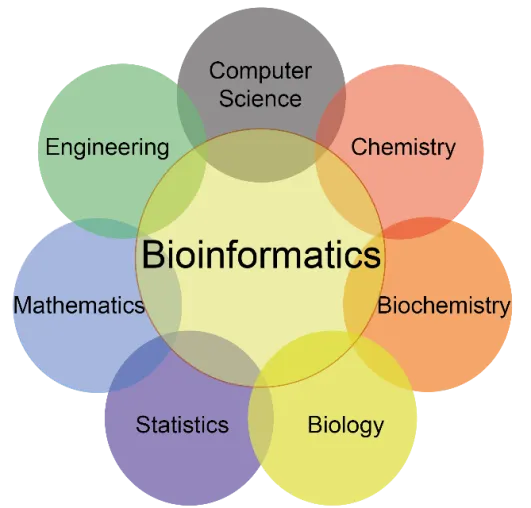
Bioinformatics is the technical backbone of pharmacogenomics and personalized medicine.
💡 Why This Research Area Is Extremely Important
• Reduces the cost and time of pharma R&D
• Improves the success rate and reduces human errors
• A major portion of future jobs will come from this area
Who Should Choose This Area?
This area is best for students who:
• Have an interest in technology along with pharmaceuticals
• Are not afraid of coding (basic level is sufficient)
• Want a future-proof career
Career Opportunities
With an AI and data background, you can become a:
• Pharma Data Analyst
• Bioinformatics Scientist
• AI-driven Drug Discovery Associate
• Clinical Data Analyst
• Research Scientist (interdisciplinary roles)
📚 Subjects & Skills Required
To excel, you should have a strong foundation in:
• Basic pharmacology & biochemistry
• Statistics (basic level)
• Bioinformatics fundamentals
Important skills:
• Excel, R, Python (basic)
• Data visualization
Research Area 10: Public Health, Pharmacoepidemiology & Health Outcomes Research
So far, we’ve talked about drugs, patients, and technology. But there’s another important question:
“What is the impact of a drug on the entire population?”
This question is answered by
Public Health, Pharmacoepidemiology & Health Outcomes Research.
This area goes beyond the individual patient and thinks at the society and population level.

What is Public Health & Pharmacoepidemiology?
Public Health research focuses on:
• Population health improvement
• Disease prevention
• Healthcare access and policy
Pharmacoepidemiology means:
• How drugs are being used in the real world
• Which drugs are being prescribed more
• What benefits and risks they are causing
Based on Health outcome research:
• Government policies are made
• Treatment guidelines are updated
• Insurance coverage is decided
💡 Why This Research Area Is Extremely Important
• Clinical trials are conducted on a limited population
• Real-world patients are diverse
• Long-term effects can only be determined through population studies
Therefore:
• Vaccine programs
• National disease control strategies
• Drug withdrawal decisions
all depend on public health data. A drug’s true value is decided in the real world, not just in trials.
Who Should Choose This Area?
This field is ideal for students who:
• Want to create a society-level impact
• Are interested in statistics, data, and trends
• Prefer policy-making and public health roles
• Are interested in population health rather than clinical labs
🎯 Career Opportunities
After this area, you can work as a:
• Public Health Researcher
• Pharmacoepidemiologist
• Health Outcomes Analyst
• WHO / NGOs / Government projects
• Health policy think-tanks
The international scope in this field is quite strong. ,
📚Subjects & Skills Required
To be strong:
• Biostatistics
• Epidemiology
• Research methodology
• Pharmacology (applied understanding)
Important skills:
• Data analysis and Report writing
• Interpretation of large datasets
• Public health communication
C. Conclusion
Whether you want to:
• Discover new drugs
• Develop better formulations
• Ensure patient safety
• Or shape healthcare policies
👉 Research awareness helps you choose the right direction.
Research isn’t just about lab work — it’s a way of thinking that transforms you
from an ordinary pharmacist into an extraordinary professional.
“You don’t need to become a researcher,
but you must think like one to succeed in pharmacy.”
📣 Call to Action
If you are a pharmacy student and:
• want career clarity
• want to explore research
• want to become future-ready
Then regularly visit 👉 edumentorashish.com
Here you will find real guidance, practical clarity, and honest mentorship.
You can also visit our YouTube channels:

If you need any help related to career development or personal mentorship, you can write to me personally at edumentorashish@gmail.com.




